Elena Perea Úbeda-Portugués
Engagement
Active learning is generally defined in the literature as any instructional method that engages student in the learning process, and requires students to perform meaningful learning activities and think about what they are doing (Prince, 2004).
It has also been described as the process of talking, writing, relating to and reflecting on what is being learned, rather than passively receiving information (Chickering & Gamson, 1987). The core components of active learning are student activity and engagement in the learning process (Prince, 2004).
Research has demonstrated that engaging students in the learning process increases their attention and focus, motivates them to practice higher-level critical thinking skills, and promotes meaningful learning experiences. Instructors who adopt a student-centered approach to instruction increase opportunities for student engagement, which then helps everyone more successfully achieve the course’s learning objectives.
How to engage our students?
Flip the classroom
Flipping the classroom is a “pedagogy-first” approach to teaching. In this approach in-class time is “re-purposed” for inquiry, application, and assessment in order to better meet the needs of the individual learners.

Employing Inclusive Teaching Strategies
Inclusive teaching means teaching in ways that do not exclude students, accidentally or intentionally, from opportunities to learn. refer to any number of teaching approaches that address the needs of students with a variety of backgrounds, learning styles, and abilities. These strategies contribute to an overall inclusive learning environment, in which students feel equally valued.
Promoting Student Engagement through Active Learning
Active learning requires students to participate in class, as opposed to sitting and listening quietly. Strategies include, but are not limited to, brief question-and-answer sessions, discussion integrated into the lecture, impromptu writing assignments, hands-on activities, and experiential learning events.
Teaching with Technology
In-classroom technologies—podium-based computers, wireless, real-time response systems (e.g., clickers), and web-based tools (e.g., blogs, online forums, wikis, podcasts, etc.)—continue to change rapidly. These tools have a high potential for supporting student learning in creative and innovative ways when properly aligned with the instructor’s learning objectives and course content.
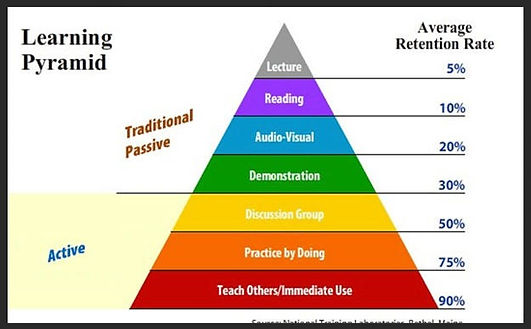
Increase motivation
Intrinsically motivated students tend to persist longer, work harder, actively apply strategies, and retain key information more consistently. Factors affecting the development of intrinsic motivation in a school setting:
-
Level of challenge offered by tasks and materials.
-
Quality and timing of feedback to students about heir work.
-
Supports and scaffolds available to learners.
-
Students’ interest in tasks and content.
-
Nature of the learning context.
Activate students knowledge
Engaged students gain knowledge and experience continually activating and extending their understanding. They apply knowledge to answer a new question or to solve a problem. Graphic organisers, concept mapping, mind mapping, thinking routines and games such as "back to the board" are very useful to activiate students knowledge.
Use cognitive strategies
Engaged students use cognitive strategies for integrating information, and communicating and representing their understanding.
Cognitive strategies are procedures that can help students succeed at higher-order tasks.
Use different groupings
When children are highly social, sharing their work frequently, they are likely to be active, interested students.
Also, as a teacher you might think an individual student or a certain group would benefit from more interaction from you.

